Agenda
- What is Sand Binder Jetting?
- Who is Sand Binder Jetting for?
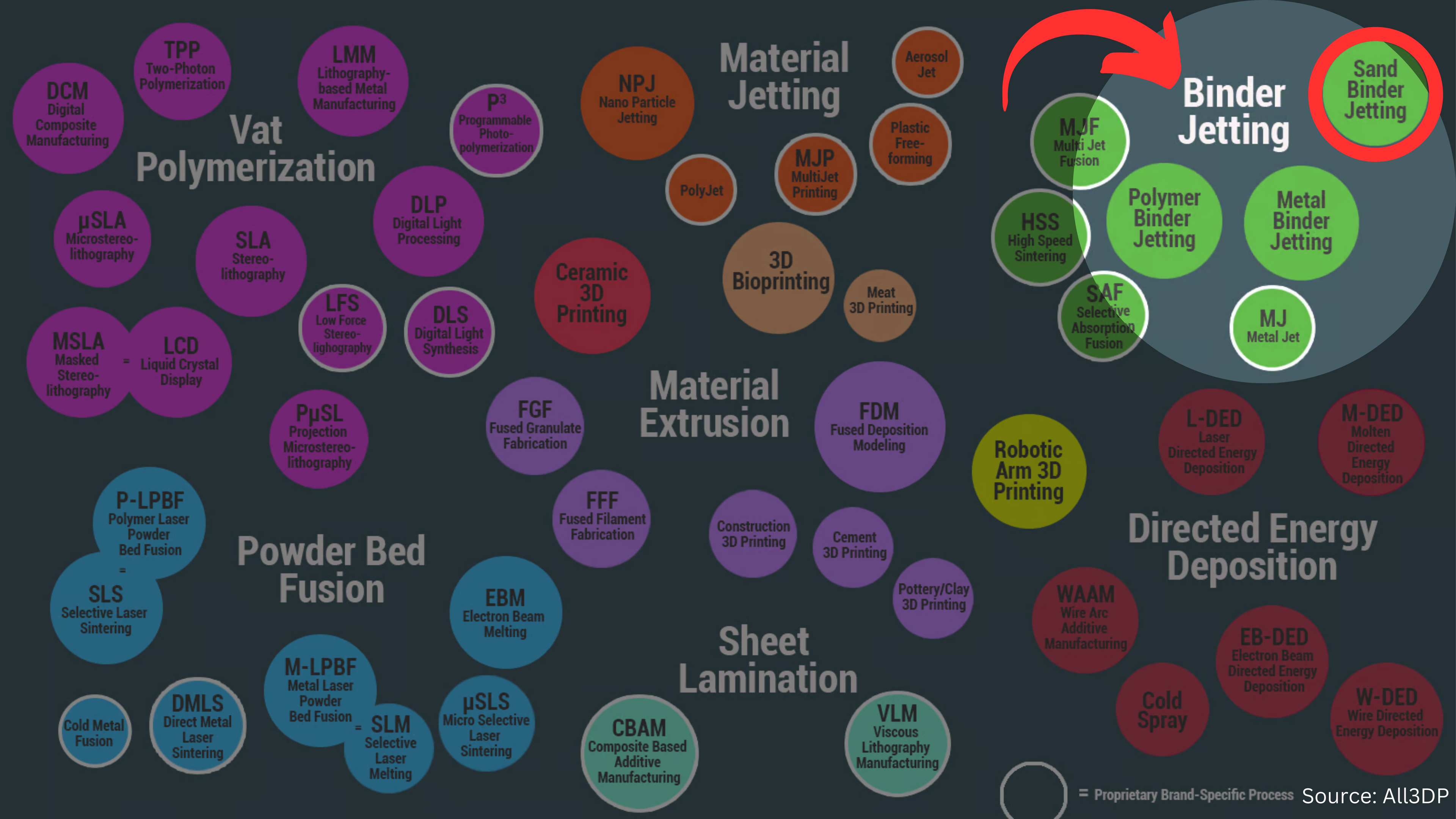
What is Binder Jetting?
Binder Jetting 3D printing uses a binding agent to selectively fuse layers of powdered material, creating detailed parts. It's ideal for complex geometries, rapid prototyping, and low-volume production without the need for molds.
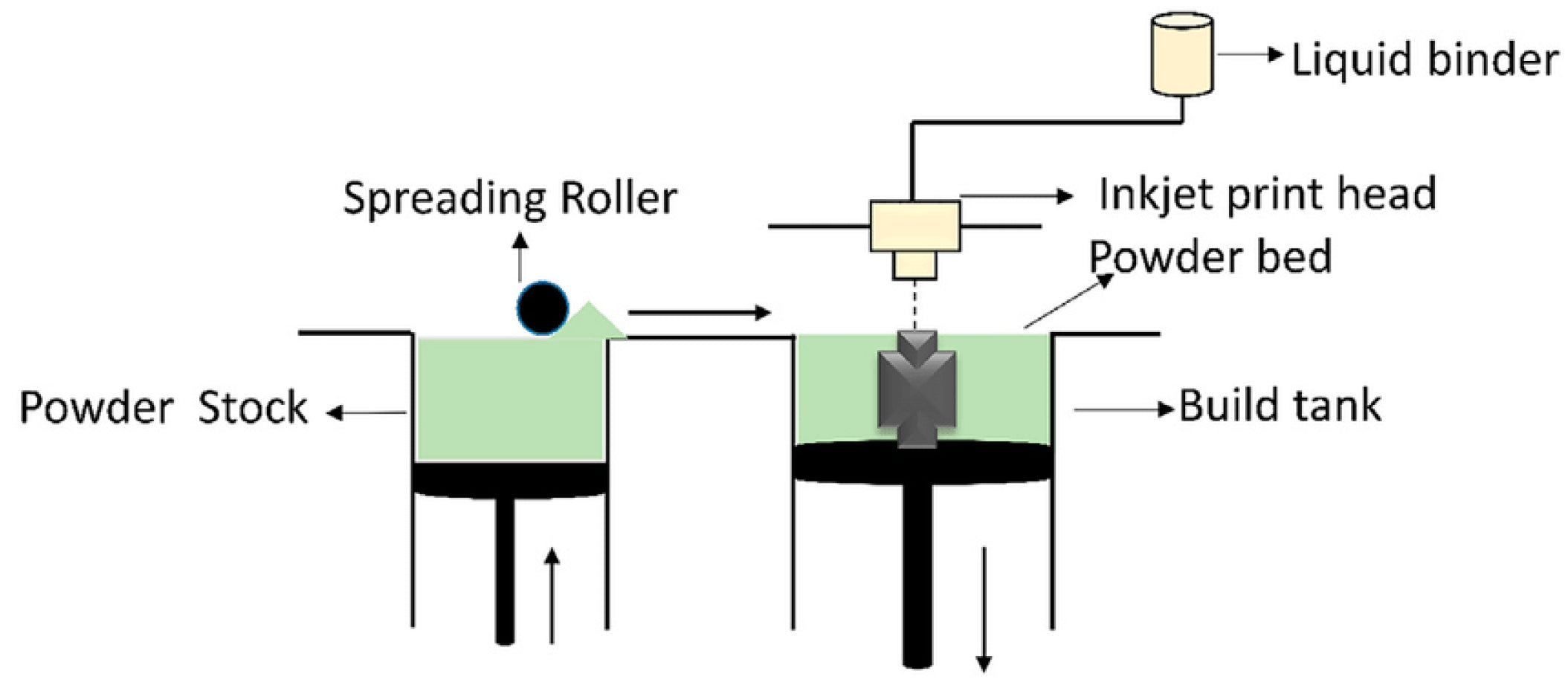
How does Binder Jetting Work?
- Layering: A thin layer of powder (metal, sand, ceramic, etc.) is spread across the build platform.
- Binding: A print head sprays a binding agent onto the powder, fusing the material where needed according to the design.
- Layer-by-Layer: The process repeats, building the part layer by layer, with each new layer of powder being fused by the binder.
- Post-Processing: After printing, the part is removed from the powder bed and undergoes post-processing like curing or sintering for strength.
Who is Sand 3D Printing for?
-
Foundries
-
Universities
-
Designers
Foundry: Metal Casting
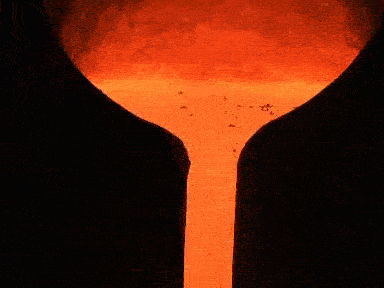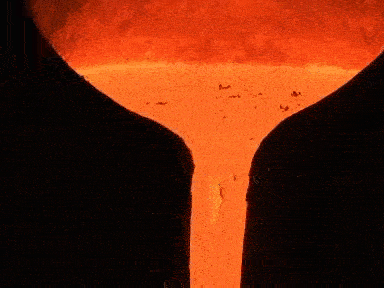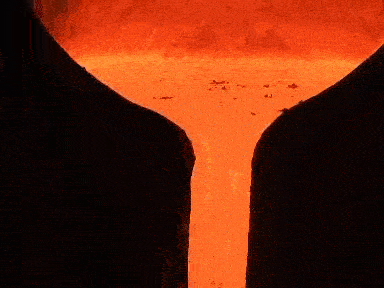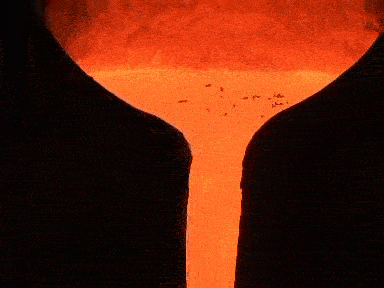
Sand molds have been used for centuries to create metal objects. In this traditional process, a pattern is pressed into the sand to form the shape, then molten metal is poured in. After cooling, the sand is removed. This technique is still widely used today in industries like automotive, aerospace, construction, and general manufacturing. However, what if you could eliminate the pattern-making step altogether and directly 3D print the sand mold?
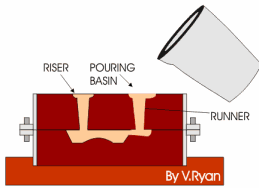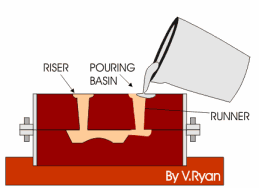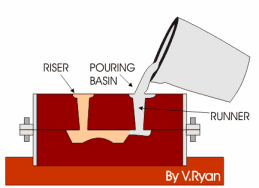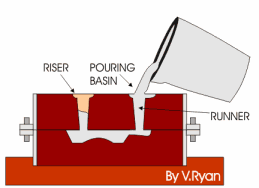
Sand Mold Metal Casting
3D sand printing (3DSP) generally employs binder jetting technology. The process begins with a digital mold file, which is converted into layer-by-layer instructions for the printer. Various CAD software tools can help create a digital mold from your part file.
In the printer, a recoater spreads a thin layer of sand on the build platform, which is then selectively bonded with a liquid bonding agent or “glue.” This process is repeated until the mold is complete. After printing, the mold is removed from the surrounding loose sand and can undergo optional surface finishing. Multiple products are often printed together in a single job box to optimize the build space.
Sand molds and cores can be manufactured with an accuracy of ±0.25 mm, allowing sand castings to achieve dimensional standards comparable to those of lost wax investment castings.
Water Pump Casing Mold and Core (Source: Aniwaa)
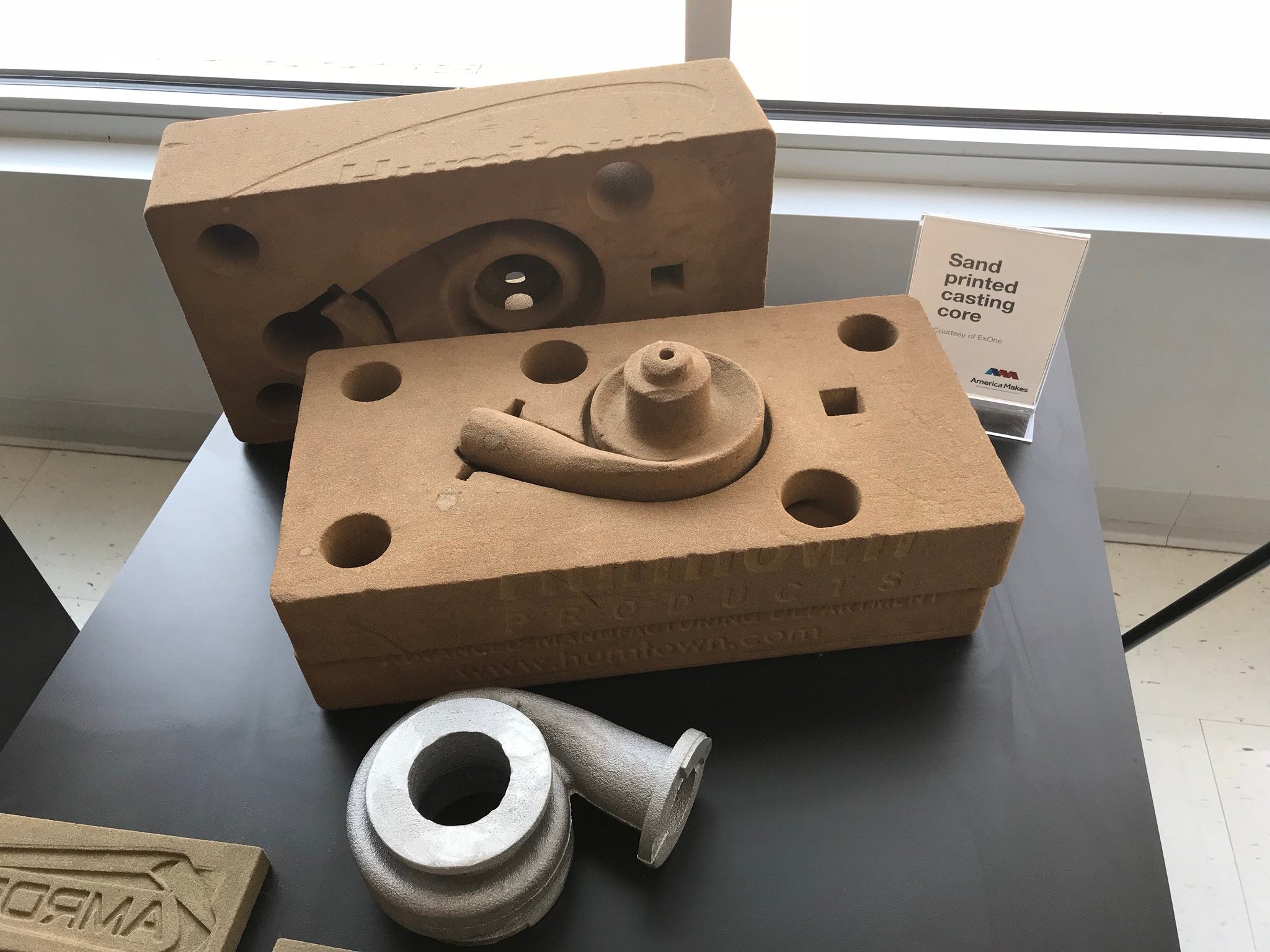

OK Foundry in Virginia uses a 3D printed sand mold to case a 1912 Velie engine block (Source: All3DP)
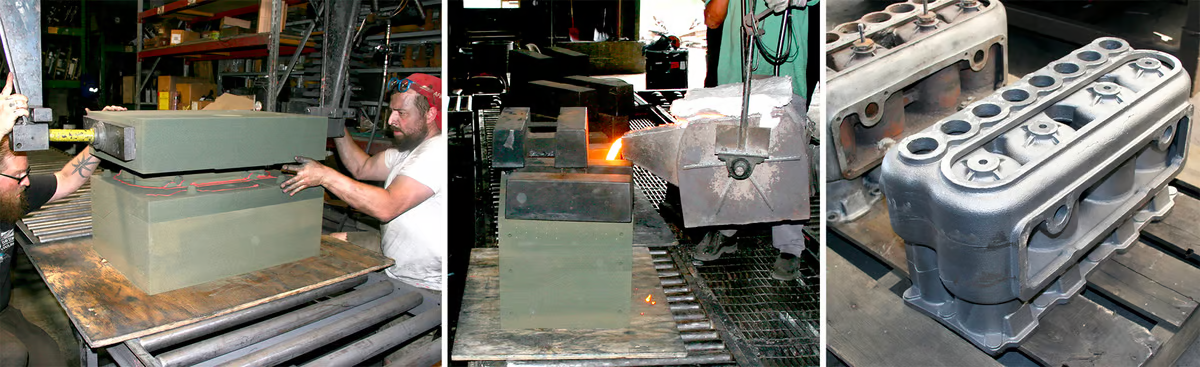
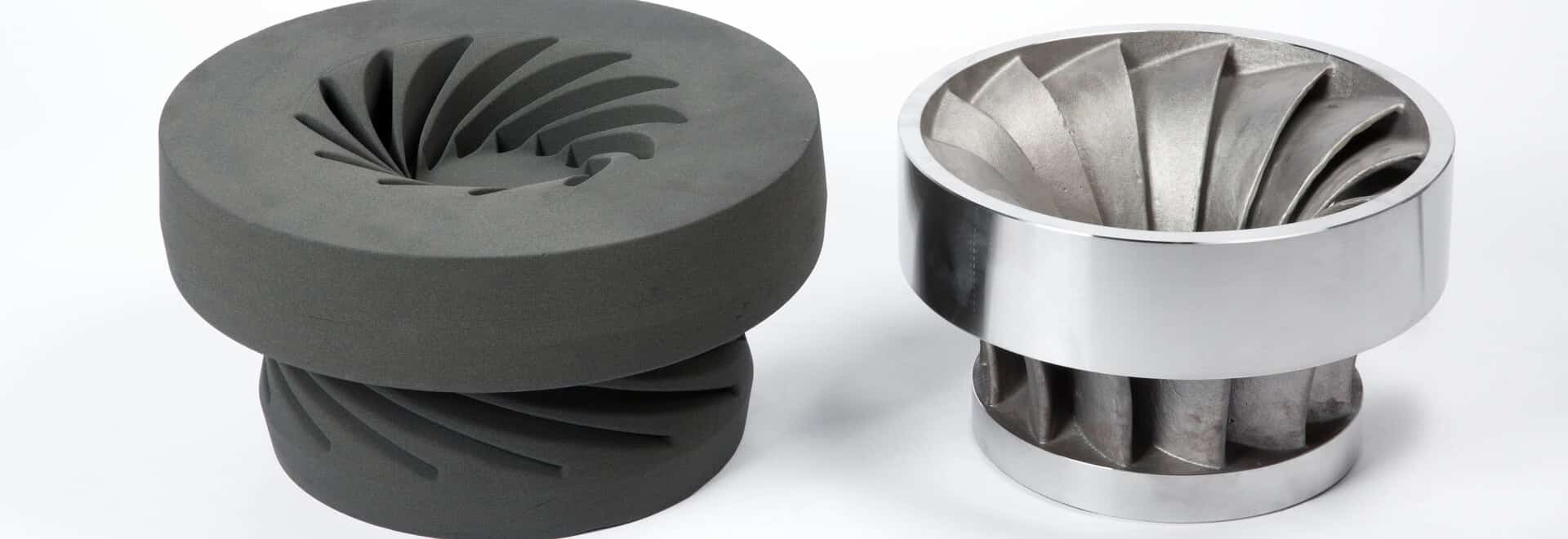
Sand Mold Vs. Final Steel Casted Part (Source: precious3d.com)

Universities & Laboratories

Sand 3D Printing can be utilized in educational institutions, particularly in engineering and manufacturing programs, for a variety of purposes

Teaching Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
Understanding Binder Jetting Technology: Students learn the principles and mechanisms behind binder jetting, including material compatibility, layering processes, and curing methods.
Digital Design and Prototyping: Using CAD software, students can design complex parts or sand molds and print them to see how their designs translate into physical objects.

Casting and Foundry Training
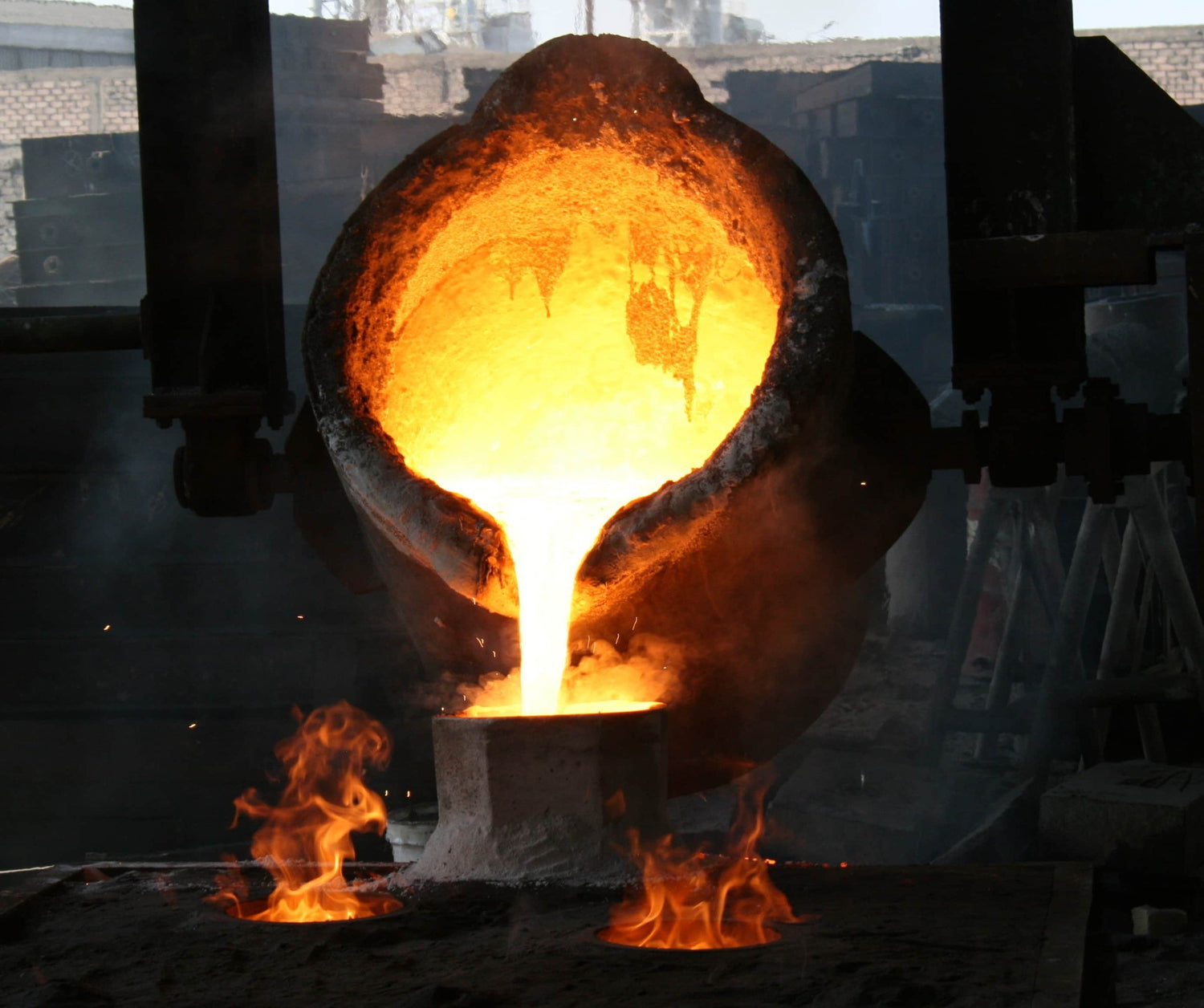
Producing Sand Molds: The machine allows students to create precise sand molds for metal casting, enabling hands-on experience in the foundry process.
Experimenting with Materials: Students can test different types of sand, resin binders, and curing methods to understand how material properties affect casting outcomes.

Research and Development
Innovating Casting Techniques: Universities use the machine to explore innovative methods for producing molds and cores, such as integrating cooling channels or complex geometries.
Studying Material Behavior: Researching how different sand compositions and binder formulas perform in industrial applications.

Interdisciplinary Applications
Art and Design: Students in design programs can use the machine to create intricate sand molds for artistic metal casting projects.
Mechanical and Civil Engineering: The machine can be used to teach structural principles by creating and testing custom shapes or components.
